n-Propyl alcohol
Agent Name
n-Propyl alcohol
Alternative Name
n-Propanol
CAS Number
71-23-8
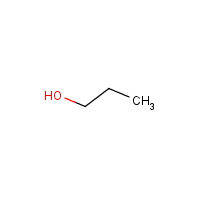
Formula
C3-H8-O
Major Category
Solvents
Synonyms
n-Propanol; 1-Hydroxypropane; 1-Propyl alcohol; Albacol; Alcohol, propyl; Alcool propilico [Italian]; Alcool propylique [French]; Ethyl carbinol; Ethylcarbinol; Optal; Osmosol Extra; Propanol; Propanol-1; Propanole [German]; Propanolen [Dutch]; Propanoli [Italian]; Propyl alcohol (natural); Propyl alcohol, normal; Propylic alcohol; Propylowy alkohol [Polish]; n-Propan-1-ol; n-Propanol; n-Propyl alcohol; n-Propyl alkohol [German]; [ChemIDplus] UN1274
Category
Alcohols (<C12)
Description
Colorless liquid with a mild, alcohol-like odor; [NIOSH]
Sources/Uses
Used as a solvent, antiseptic, and chemical intermediate; [ACGIH] Used as a solvent in inks, pesticides, and lacquers; [HSDB]
Comments
A mucous membrane irritant similar to isopropyl alcohol, n-propyl alcohol produces narcosis in animals inhaling high concentrations. It causes severe liver injury in chronic feeding studies of laboratory animals. [ACGIH] Irritating to the eyes; Inhalation of high concentrations can cause CNS depression; [ICSC]
Biomedical References
Exposure Assessment
Skin Designation (ACGIH)
Insufficient data
TLV (ACGIH)
100 ppm
PEL (OSHA)
200 ppm
IDLH (NIOSH)
800 ppm
Excerpts from Documentation for IDLHs
Human data: Mild irritation of the eyes, nose, and throat have been reported at 400 ppm [Nelson et al. 1943]. It has been reported that 5,700 mg/kg is the lethal oral dose [Durwald and Degen 1956]. [Note: An oral dose of 5,700 mg/kg is equivalent to a 70kg worker being exposed to about 94,000 ppm for 30 minutes, assuming a breathing rate of 50 liters per minute and 100% absorption.]
Vapor Pressure
21 mm Hg
Odor Threshold Low
0.03 ppm
Odor Threshold High
41 ppm
Lethal Concentration
LCLo (rat) = 4,000 ppm/4H
Explanatory Notes
Detection odor threshold from AIHA (mean = 5.3 ppm); Flash point = 23 deg C; VP from HSDB;
Half Life
No reports found; [TDR, p. 1052]
NFPA
may ignite at ambient temp
Adverse Effects
Neurotoxin
Acute solvent syndrome
Hepatotoxin
Hepatoxic (a) from occupational exposure (secondary effect) or (b) in animal studies or in humans after ingestion
ACGIH Carcinogen
Not Classifiable
Diseases, Processes, and Activities Linked to This Agent
Diseases
Occupational diseases associated with exposure to this agent:
Processes
Industrial Processes with risk of exposure: