Rotenone
Agent Name
Rotenone
CAS Number
83-79-4
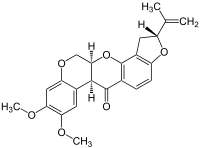
Formula
C23-H22-O6
Major Category
Pesticides
Synonyms
Tubatoxin; Derris; Noxfish; Foliafume; Nusyn-Noxfish; PB-Nox; Barbasco;Cube root; Cubor; Dactinol; Deril; Dri-Kil; Extrax; Fish-Tox; Haiari; Mexide; Nicouline; Paraderil; Pro-Nox fish; RO-KO; Ronone; Rotefive; Rotefour; Rotessenol; Synpren; Prenfish; Nusyn; Chem-Fish; Cuberol; Fish Tox; Noxfire; Rotacide; Sinid; Tox-R; Curex Flea Duster; Derrin; Cenol Garden Dust; Chem-Mite; Cibe Extract; Green Cross Warble Powder
Category
Other Insecticides
Description
Colorless to red, odorless, crystalline solid. [insecticide] [NIOSH]
Sources/Uses
Used to kill insects in gardens and on pets; the emulsion form is used to kill fish in lakes and ponds; [EXTOXNET] Derived from the East Asian Derris (tuba) plant; Used in agricultural fields and orchards; Also used to control fire ants, household insects, scabies and head lice in humans, and other ectoparasites in domestic animals; [Krieger, p. 135]
Comments
Formulations for home use are classified as "slightly toxic." The emulsified concentrate is classified as "highly toxic." Only certified applicators can use rotenone on cranberries and for fish control. [EXTOXNET] Skin and respiratory irritation has been reported after occupational exposure. [EPA Pesticides] Poisoning by ingestion in humans may result in convulsions and coma. [ACGIH] Liver and kidney injury may occur after ingestion. [ICSC] Rotenone is used in an experimental animal model of Parkinson's syndrome, but the large doses used are not likely to be relevant to occupational exposure levels. [Reference #2] Decomposes within days when exposed to light and air; No evidence to support a causal relationship between rotenone and Parkinson's disease; In a fatal poisoning case, the estimated oral dose was 50 mg/kg, and the symptoms were coma and respiratory arrest within 8.5 hours of ingestion; [Krieger, p. 135-41]
Reference Link #1
Biomedical References
Exposure Assessment
Skin Designation (ACGIH)
Insufficient data
TLV (ACGIH)
5 mg/m3
PEL (OSHA)
5 mg/m3
IDLH (NIOSH)
2500 mg/m3
Excerpts from Documentation for IDLHs
Basis for original (SCP) IDLH: ACGIH [1971] reported that Lehman [1949], on the basis of his own work and a literature survey, estimated the fatal human oral dose to be about 200 grams. Accordingly, this is a relatively nontoxic compound for humans, and thus respirators have been assigned based on the assigned protection factor . . . Basis for revised IDLH: No inhalation toxicity data are available on which to base an IDLH for rotenone. Therefore, the revised IDLH for rotenone is 2,500 mg/m3 based on acute oral toxicity data in humans [Lehman 1949] and being 500 times the NIOSH REL and OSHA PEL (500 is an assigned protection factor for respirators and was used arbitrarily during the Standards Completion Program for deciding when the "most protective" respirators should be used for particulates).
Vapor Pressure
0.0008 mm Hg
Reference Link #2
Adverse Effects
Neurotoxin
Parkinsonism
Hepatotoxin
Hepatoxic (a) from occupational exposure (secondary effect) or (b) in animal studies or in humans after ingestion
ACGIH Carcinogen
Not Classifiable
Diseases, Processes, and Activities Linked to This Agent
Processes
Industrial Processes with risk of exposure: