Sulfuryl fluoride
Agent Name
Sulfuryl fluoride
CAS Number
2699-79-8
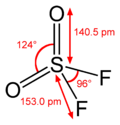
Formula
F2-O2-S
Major Category
Pesticides
Synonyms
Sulfur difluoride dioxide; Vikane®; [NIOSH] UN2191
Category
Fumigants
Description
Colorless, odorless gas. [insecticide/fumigant] [Note: Shipped as a liquefied compressed gas.] [NIOSH]
Sources/Uses
Used as a structural fumigant to kill termites; [ACGIH]
Comments
Concentrations inside fumigated structures are as high as 4000 to 40,000 ppm. Inhalation exposure may cause pulmonary edema. [ACGIH] Because sulfuryl fluoride is heavier than air, workers who re-enter a treated area are at risk for fatal hypoxia. Muscle twitching and seizures have been reported after acute poisoning. [EPA Pesticides, p. 161] Possible frostbite from contact with liquid; [NIOSH] The exact toxic mechanism is not known, but increased fluoride ion concentrations have been found in poisoned victims. Systemic fluorosis may result from sulfuryl fluoride poisoning. Fluoride can cause hypocalcemia and hyperkalemia with secondary arrhythmias and central nervous effects including agitation, tetany, and seizures. [AHLS, p. 266-7] This gas has no warning properties, but chloropicrin is often added. After chronic inhalation studies, animals have evidence of liver injury. [HSDB] See "FLUORIDES."
Reference Link #1
Biomedical References
Exposure Assessment
Skin Designation (ACGIH)
Insufficient data
TIH
Yes
TLV (ACGIH)
5 ppm
STEL (ACGIH)
10 ppm
PEL (OSHA)
5 ppm
IDLH (NIOSH)
200 ppm
Excerpts from Documentation for IDLHs
Other animal data: It has been reported that less than 5% mortality resulted from exposure for 3 hours to 1,000 ppm [Taxay 1966].
Lethal Concentration
LC50 (rat) = 991 ppm/4H
Explanatory Notes
Not combustible; [CHEMINFO]
Reference Link #2
Adverse Effects
Toxic Pneumonitis
Yes
Neurotoxin
Other CNS neurotoxin
Hepatotoxin
Hepatoxic (a) from occupational exposure (secondary effect) or (b) in animal studies or in humans after ingestion
Diseases, Processes, and Activities Linked to This Agent
Diseases
Occupational diseases associated with exposure to this agent:
Processes
Industrial Processes with risk of exposure: