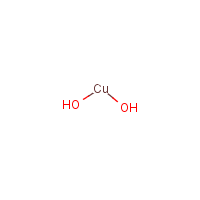
Copper(II) hydroxide
Agent Name
Copper(II) hydroxide
Alternative Name
Cupric hydroxide
CAS Number
20427-59-2
Formula
Cu-H2-O2
Major Category
Metals
Synonyms
Blue Copper; Blue Shield; Blue Shield DF; Champ; Champ Formula II; Comac Parasol; Copper blue; Copper dihydroxide; Copper hydroxide (Cu(OH)2); Copper(2+) hydroxide; Cupravit Blue; Cupravit blau; Cupric Hydroxide Formulation Grade Agricultural Fungicide; Cupric hydroxide; Cuzin; Funguran OH; Hydrocop "T"; KOP Hydroxide; KOP Hydroxide WP; Kocide; Kocide 101; Kocide 101PM; Kocide 2000; Kocide 220; Kocide 404; Kocide Copper Hydroxide Antifouling Pigment; Kocide Cupric Hydroxide Formulation Grade; Kocide DF; Kocide LF; Kocide SD; Kuprablau; Nu-Cop; Parasol; Spin Out FP; Technical Hydrox; Wetcol; [ChemIDplus]
Category
Metals, Inorganic Compounds
Description
Blue to green solid; [HSDB] Insoluble in water; Decomposes to Copper (II) oxide in hot water; [Ullmann]
Sources/Uses
Used to make rayon, battery electrodes, fungicides/insecticides, and other copper salts; Also used as a dye mordant, paper colorant, pigment, feed additive, and catalyst; [Merck Index]
Comments
Toxic after ingestion or inhalation; [Hawley] A skin, eye, and respiratory tract irritant; [MSDSonline] Acute copper poisoning after ingestion can cause liver injury, methemoglobinemia, and hemolytic anemia. Acute renal failure may result, secondary to massive hemoglobinuria. [Goldfrank, p. 1259] See "Copper."
Biomedical References
Exposure Assessment
TLV (ACGIH)
1 mg/m3, as Cu
PEL (OSHA)
1 mg/m3, as Cu
MAK
0.01 mg/m3, respirable fraction (Cu, inorganic cmpnds)
IDLH (NIOSH)
100 mg/m3, as Cu
Adverse Effects
Anemia
Hemolytic anemia
Methemoglobinemia
MetHgb is secondary toxic effect
Hepatotoxin
Hepatoxic (a) from occupational exposure (secondary effect) or (b) in animal studies or in humans after ingestion
Nephrotoxin
Yes
Diseases, Processes, and Activities Linked to This Agent
Processes
Industrial Processes with risk of exposure: